Neurofeedback training is a big change in how people think about brain health and how they look for brain therapy. The activity of billions of neurons in the brain is responsible for everything we think, feel, and do. As a result, brain waves or EEG are created (Electroencephalography). We train these brain waves through neurotherapy.
Neurofeedback brain training is a type of biofeedback that gives immediate, real-time feedback on brain activity and uses operant training to reinforce a healthy brain. Neurotherapy is another name for neurofeedback. It measures the subject’s or patient’s brain waves and gives him or her feedback signals to teach him or her how to control how his or her brain works. In other words, biofeedback changes the brain signal into a wave, which causes the brain to calm down. Most of the time, the feedback is in audio or video form. Are you interested to become a neurofeedback practitioner? Checkout our website to learn more.
What are EEG and QEEG?
EEG analysis is the process of analyzing and evaluating an EEG (brain waves) that was taken correctly using a number of mathematical and statistical methods. It helps you figure out how your brain helps you do things. QEEG also finds out how brainwaves in different places relate to each other. This gives a way to measure how similar communication is in terms of power, speed, and consistency. We can learn how the brain helps us think and feel, and this helps us come up with a way to directly train the brain.

Most of the time, the processed EEG is turned into color maps of how the brain works. These are called “brain maps.” When we talk about brain maps, looking back at the brain helps us understand it better so we can work on therapy. There are four lobes in the brain: the frontal lobes, the temporal lobes, the parietal lobes, and the occipital lobes. The cortex is the name for all of these lobes together. Also, the prefrontal cortex, the motor strip, and the sensory motor strip are two specialized parts of the brain.
Neurofeedback Techniques
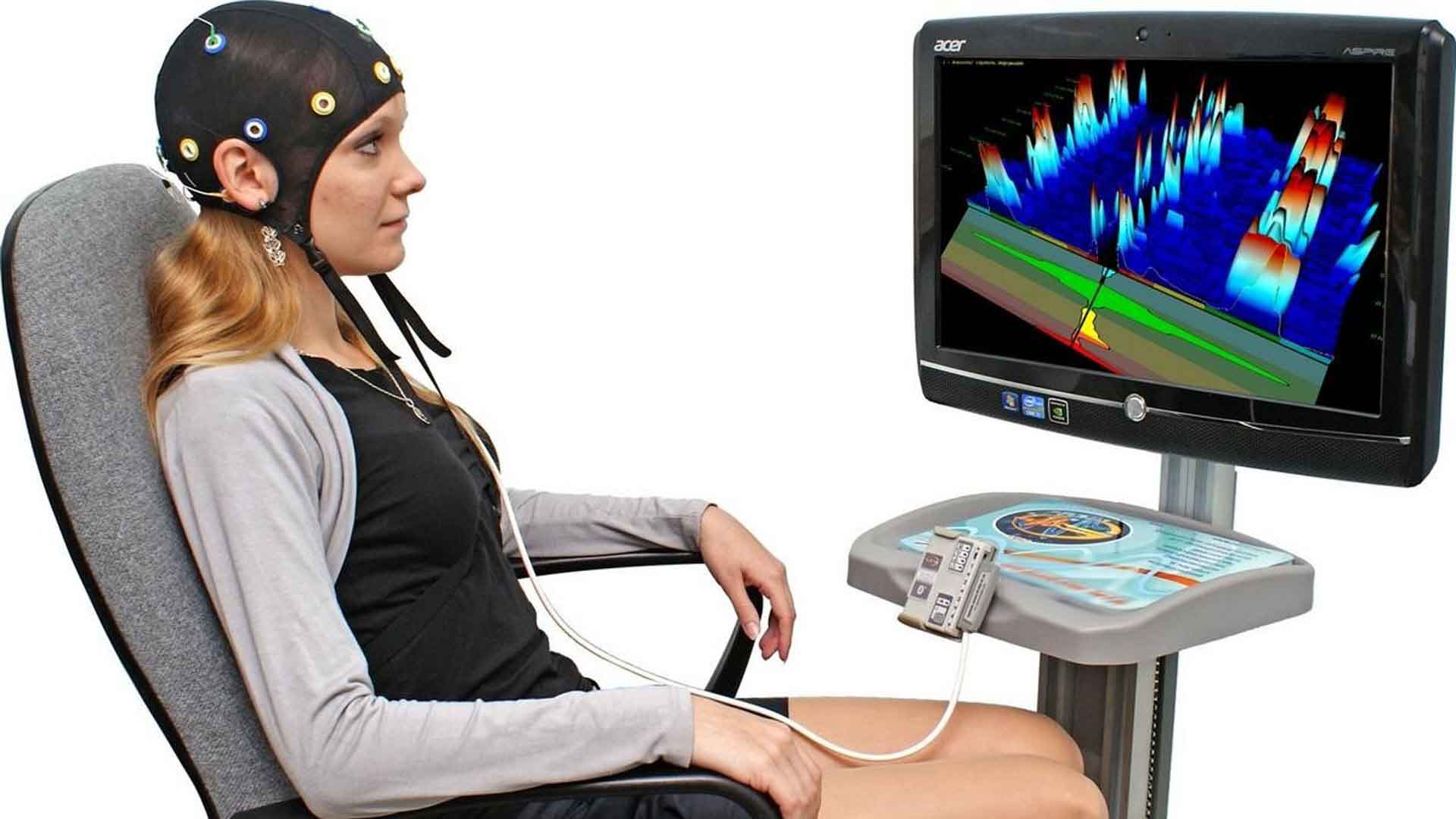
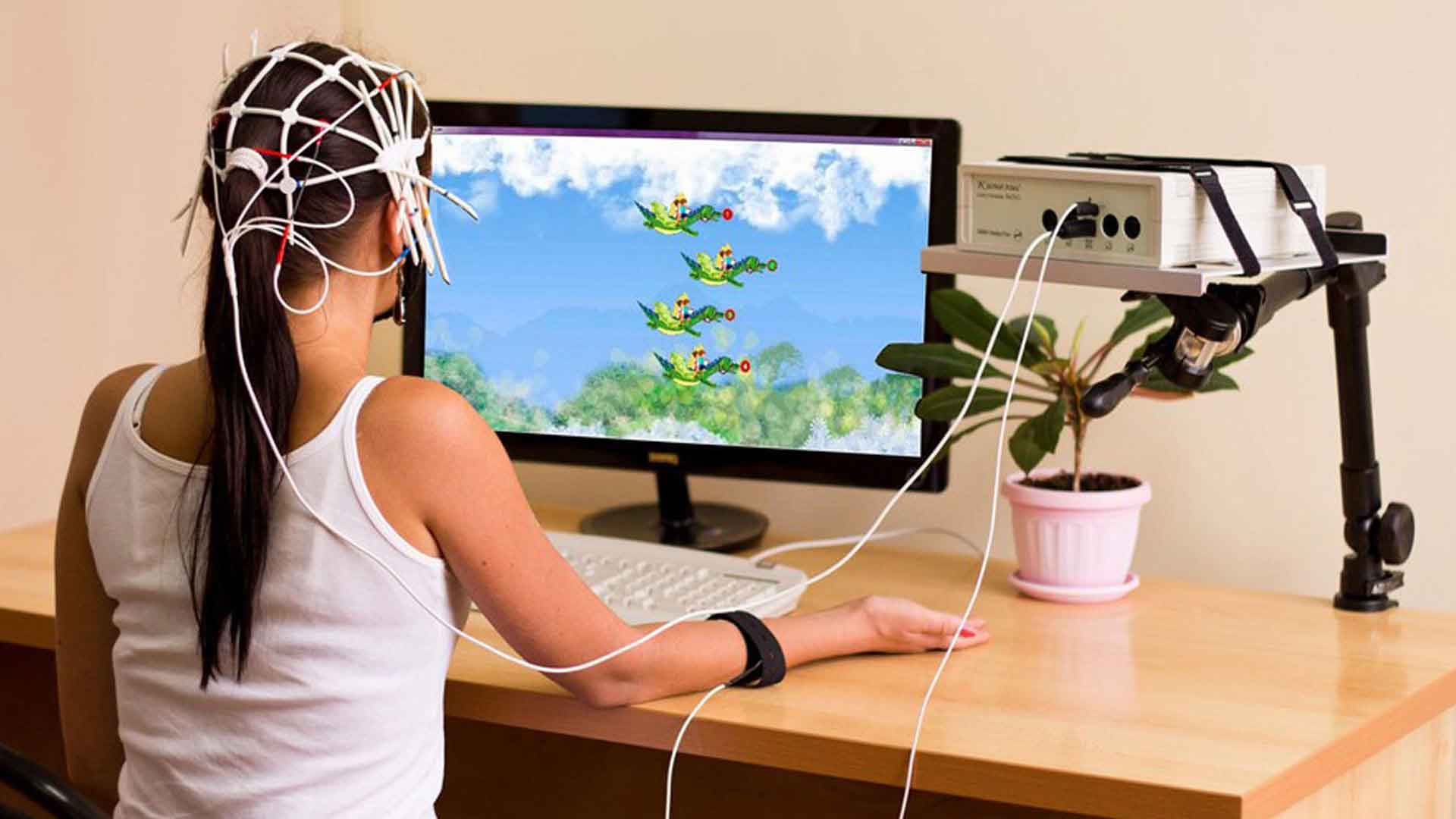
During a neurotherapy session, you will most likely sit in a chair with electrodes on your head. There isn’t any pain at all. It’s like a doctor using a stethoscope to listen to your heartbeat.
While the EEG records the electrical impulses in your brain, your therapist will guide you through a few simple exercises. Depending on your therapy, you may be asked to look at pictures on a screen, play a video game, or listen to music.
Most neurotherapy sessions last between 30 and 60 minutes. Standard neurotherapy usually takes 30 to 40 sessions. How many sessions someone needs depends on them, but it’s rare for someone to need more than 40.